Bad quality / network and bandwidth
The quality of the network components and end devices involved is ultimately decisive for the quality of Voice over IP telephone calls. These have a significant influence on interference factors such as latency, jitter and packet loss. Private users and companies should take this into account when selecting their network components.
Possible malfunctions that may occur:
- Connection termination «Call disconnection»
- Metallic speech «Robot voice»
- Echo «Own voice audible»
- Interruptions of the audio «Dropouts, stuttering»
- No audio «Codec, firewall, NAT traverse»
- No signaling «Transport protocol TCP/UDP»
The problem can occur on both sides, on your and / or on the other party’s side. If you have the problem on multiple calls from / to different parties, it is probably on your side.
Problems with the voice quality
The best practice is to perform PING tests, especially in case of voice quality issues. Make sure you run the tests over the same network of your VoIP device / client.
You will learn how much packet loss and response time your network requires for our network.
The packet loss should be 0% and the response time should be less than 30 ms.
Also run a tracking route to find out how many routes you go through to reach our network.
Perform a ping / trace route
What is the ping doing?
- Resolves the IP of a domain
- Checks if the other side is reachable
- Displays the connection quality (response time and packet loss)
PING sips.peoplefone.ch (95.128.80.3): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=0 ttl=53 time=9.332 ms 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=8.895 ms 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=2 ttl=53 time=8.827 ms 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=3 ttl=53 time=9.268 ms 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=4 ttl=53 time=9.038 ms 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=5 ttl=53 time=8.946 ms 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=6 ttl=53 time=9.310 ms 64 bytes from 95.128.80.3: icmp_seq=7 ttl=53 time=9.040 ms --- sips.peoplefone.ch ping statistics --- 8 packets transmitted, 8 packets received, 0.0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 8.827/9.082/9.332/0.184 ms
What does the trace routing do?
- Resolves the IP of a domain
- Shows the routes between you and the destination
- Displays the time that each hop has taken
traceroute to sips.peoplefone.ch (95.128.80.3), 64 hops max, 52 byte packets 1 192.168.43.1 (192.168.43.1) 6.455 ms 5.002 ms 7.254 ms 2 192.168.43.127 (192.168.43.127) 219.503 ms 356.936 ms 46.440 ms 3 192.168.43.77 (192.168.43.77) 19.922 ms 27.107 ms 27.237 ms 4 1787.eth-trunk20.zhbmb00p-cgn002.bluewin.ch (213.3.229.78) 31.624 ms 23.541 ms 21.340 ms 6 213.3.229.6 (213.3.229.6) 34.219 ms 23.231 ms 29.420 ms 7 i79zhb-041-bun1.bb.ip-plus.net (138.187.129.25) 38.026 ms 33.289 ms 28.355 ms 8 193.247.171.142 (193.247.171.142) 40.578 ms 29.154 ms 50.009 ms 9 zrh01-fw-c1-p1.peoplefone.net (185.190.124.9) 29.922 ms 19.576 ms 39.269 ms 10 pbxs.peoplefone.ch (95.128.80.3) 32.976 ms 19.315 ms 36.730 ms
For Windows
Search for «Command Prompt» in the «Start Menu» and open it. Run one of the following commands to customize the domain. You can stop the command with «CTRL + C».
ping -t sips.peoplefone.ch
tracert sips.peoplefone.ch
For macOS
Open the “Terminal” from the «Utilities» application folder. Run one of the following commands to customize the domain. You can stop the command with «CTRL + C».
ping sips.peoplefone.ch
traceroute sips.peoplefone.ch
Result from your tests
If you are unable to perform the test.
Check the registrar domain spelling
Check your Internet connection and DNS server
For the correct use of our services, the response time should not exceed 30 ms
What you need to know
It does not matter if the call is incoming or outgoing.
For your Internet connection:
- What you hear – Download
- What you say – Upload
What can I do about this
Specify bandwidth for VoIP
Ensure that there is always sufficient bandwidth available in the network for telephony. This is helped, for example, by reserving a minimum bandwidth for VoIP and prioritization functions in the switches such as Class of Service «CoS», port prioritization, service prioritization and IEEE 802.1q/Q support. According to the labeling of the voice packets, quality-of-service mechanisms «QoS» then take effect in the switches to give voice data priority over less time-critical data such as e-mails in case of doubt.
Creating a VLAN for telephony
A Virtual Local Area Network «»”VLAN” is a logical subnet within a switch or an entire physical network. It can extend across multiple switches. A VLAN separates physical networks into subnets by ensuring that VLAN-capable switches do not forward frames «Data packets» to another VLAN «Although the Subnets may be Connected to common Switches».
Test the Internet speed of the line
To get general information about the existing internet line, we recommend to run the speed test with https://www.geschwindigkeit.ch. Any other will do of course, maybe compare our recommended one with the one of your internet provider «if available». It is important that there are no packet losses, which would generally indicate a rather poor line or problems.
Test response times (latency)
With a ping on one of our servers, you will receive a response from our proxy server. A roughly always constant response time is very good for communication via Voice Over IP.
peoplefone Proxys
Depending on whether you have a standard account or a peoplefone HOSTED account, you have to ping the right proxy accordingly. Thus you will get a response back from our infrastructure.
- sips.peoplefone.ch – «SIP Trunk / Standard Account».
- pbxs.peoplefone.ch – «peoplefone HOSTED»
Windows
Press the Windows and R keys on your keyboard and type «CMD», then press Enter
Enter the command «ping -t sips.peoplefone.ch»
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=9ms TTL=54
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=9ms TTL=54
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=9ms TTL=54
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=9ms TTL=54
If the times differ significantly from each other, usually from about 23ms, then this indicates typical irregularities in the network, or the latency times are very high and can cause problems and disruptions in Voice over IP telephony. The lower the value, the faster the response times and the better the performance.
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=37ms TTL=54
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=215ms TTL=54
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=112ms TTL=54
Reply from 95.128.80.8: bytes=32 time=62ms TTL=54
With CTRL-C you can cancel the operation or simply close the Command window
Appel / MacOS
- If you have a MAC, then you can start the terminal under “Applications” “Utilities” “Terminal”
- Then enter “ping pbxs.peoplefone.ch” without brackets.
- With CTRL-C you can cancel the process or just close the command window.
Codec
Codecs, as the name implies, are used to «encode» and «decode» the audio. This is simply the technical term for translating a signal into another format. In this case, we take the analog audio signal from the microphone and translate it into a digital signal that can be sent over the Internet.
And vice versa for incoming audio.
Both sides negotiate to use one of these codecs to successfully establish a call.
This means that both sides of a call must each support at least one of these codecs.
Supported codecs
Peoplefone supports calls with the following codecs:
- G.711a (also known as “a-law” or “PCMA”)
- G.711u (also known as “u-law” or “PCMU”)
- G.722
- G.729a
G.711a/u are the most commonly used codecs and have a quality comparable to normal landline calls
G.711a is commonly used in the Europe/Asia-Pacific regions, while G.711u is more commonly used in regions from the Americas. Although similar, they are not interchangeable, so we recommend enabling both for best compatibility.
G.722 is an HD codec that gives you better quality, but also requires more bandwidth. As mentioned above, both sides must support this codec.
G.729a is a codec that has a special compression algorithm with the aim of achieving the same quality as G.711a/u, but with less bandwidth requirements. Due to the algorithm, this is a proprietary codec, meaning it requires a paid license and is therefore often sold as an add-on in otherwise free VoIP software products, while many desk phones have it licensed from the manufacturer and as such it is available to the phones without additional purchase.
Possible reasons for a busy network
Internet
Here are a few examples that could well cause problems with Voice Over IP telephony:
- No good Internet coverage in the region
- Not the performance promised by the Internet provider «Slow and High Latency».
- Not the optimal hardware
- Internet subscription too small
Server and services
Servers or services that perform certain tasks in the network can accordingly also rob performance in the respective network. In the example of an FTP server where files are copied back and forth, performance is needed for this time in the network. Exactly the same for example with a WSUS «Windows Server Update Service» which delivers the updates for the clients over the noon time after the download, then it could come under circumstances to performance fluctuations in the network. But also accesses to NAS, backup system etc. can be performance robbing in the network. Even with a «glass connection», bottlenecks can occur. If the tube becomes too small, no more packets get through.
- FTP
- Webserver
- WSUS
- NAS
- Backupsysteme
- DNS
- etc.
Hardware
It doesn’t always have to be a server or service that is to blame for poor performance, the clients / PCs downloading an update may also be to blame for degraded network performance. However, it may also be that a cascading of switches, the cabling or even a defective switch port is causing the problems.
- Headphones and microphone
- Client Computers «Client Updates»
- Cascading «Switch1 → Switch2 → Switch3»
- Directional beam antenna
- Routers, Firewall, Switch
- Cabling cables
- «Cat5, Cat6»
- etc.
Programs / Applications
Programs and applications can also require performance in the network, the longer the data moving in the network, the larger it becomes. Here are just a few possible applications that are performance guzzlers:
- Office365
- Video / Audio-Streaming
- Virus program security checks
- Video and image editing
- CAD
- Heavy files
- usw.
Technical terms
Bandwidth
For a good quality call, not much bandwidth is needed, 100 kilobytes permanent up/download is sufficient. However, this must be permanently available for almost (real-time communication). The bandwidth required for the transmission of voice data is determined, among other things, by the codec used and its bit rates, the payload per packet.
CAUTION: It is ultimately essential that there is always sufficient bandwidth available in the network for telephony.
Latency
The delay in the transmission of data packets, also called network packet delay, describes the time required for a data packet to travel from its starting point through the network to its destination. Each station along the way, such as switches, routers, firewalls or jitter buffers, as well as the length of the path itself, increases this value.
Voice codecs
In most cases, the encoding process does not digitize the analog signals without loss, but instead involves dynamic range reduction of the analog signal as well as data compression of the digital signal, which, depending on the extent and method, leads to quality losses when the digital data stream is converted back into the analog signals. Not only the sound quality can be affected, but also the continuity of the playback. This results in a reduction of the bandwidth necessary for the transmission of the digital signal. Please note the supported codecs of peoplefone and also in some cases the order, we always recommend to start with the smallest «quality».
Jitter
In network technology, jitter refers to the variance in the runtime of data packets from the sender to the receiver from the point of view of the application. Jitter of more than 20 milliseconds can lead to quality problems in voice transmission with an assumed packet payload of 20 milliseconds of voice data.
Package loss
Packet loss means that a sender sends packets on their way that do not arrive at the receiver due to network problems. In practice, it is difficult to identify packet loss as the cause of a problem. This is because each codec handles packet loss differently. For example, if the loss rate is identical, the perceived speech quality of a codec with data compression could be better than a codec that occupies the entire bandwidth.
Package order
Incorrect sequence of incoming data packets has an effect similar to packet loss for voice and video transmissions. If a packet arrives out of sequence, it is discarded by the end device by default. This is because it is obviously not sensible to play back voice data in the wrong order.
Transcodierung
Transcoding is the conversion of voice signals during the transition from a TDM «Time-Division Multiplexing» – to an IP network and vice versa. If the voice data has to be converted several times during a call – for example, because both subscribers are telephoning internally via IP, but the call is being transferred via the fixed network – the voice quality is reduced with each transition. Ultimately, this can only be solved by routing calls as intelligently as possible.
Echo
There are two causes for the notorious echo in VoIP calls: Acoustic echo occurs when feedback occurs between the speaker/earpiece and the microphone on a telephone. Line echo, on the other hand, occurs when there is a difference in impedance at the transition between a two-wire and four-wire network, during signal conversion between a TDM “time-division multiplexing” bus and the LAN, or when there is unequal impedance between a headset and its adapter.
SIP Call Session
SIP stands for Session Initiation Protocol and is a network protocol that is frequently used to set up telephone calls via VoIP (Voice over IP). It is one of many signaling protocols that enable the establishment and termination of a call (session) between two or more participants, but is used particularly frequently in IP telephony.
Functionality
The task of the protocol is comparable to that of a telephone operator at the switchboard in the early days of telephony. Its task was to establish or terminate the connection of a call between two subscribers, without, however, being responsible for other aspects of the call. It is also possible to establish an encrypted connection thanks to Session Initiation Protocol Secure, or SIPS for short.
SIP signaling is not responsible for the actual transmission of voice data. Rather, this runs separately via a number of other protocols such as RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol), which handles the transmission of audio and video data – also encrypted as SRTP – and SDP (Session Description Protocol), which contains information about IP addresses and ports and negotiates the use of corresponding codecs.
Text-based and comparable to HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) or SMTP, SIP is much more flexible and easier to use than, for example, H.323. Similar to HTTP, the Session Initiation Protocol also works with URIs (Universal Resource Identifiers) to uniquely identify users. This similarity also helps integration with other Internet and local network applications. Most end devices with an Internet connection – including IP phones, gateways and smartphones – are now able to communicate with each other via SIP.
The protocol developed by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) is defined in RFC 3261. This is very significant for VoIP telephony, because the definition of methods and functions of this standard, as well as its consistent further development, allows a wide variety of uses – regardless of the operating system or IT infrastructure. Proprietary systems, on the other hand, exhibit much greater uncertainty as to whether they will always function in the same way. The digitization and mobilization of companies in particular makes SIP a suitable standard protocol for communication from different locations via different end devices and exploits considerable economies of scale in the process.
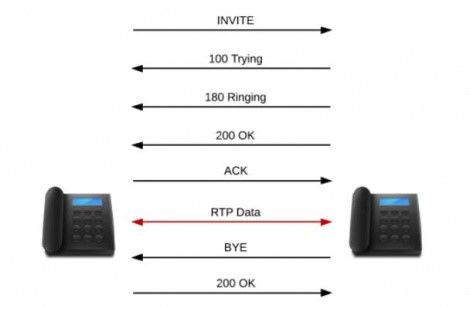
Call setup
- The calling telephone sends an INVITE.
- The called telephone sends back an information response 100 – Trying
- When the called phone rings, an answer 180 – ringing – is sent back
- When the caller answers the phone, the called phone sends an answer 200 – OK
- The calling telephone answers with ACK – Confirmation ACK – Confirmation
- Now the actual conversation is transmitted as data via RTP RTP
- When the calling person hangs up, a BYE request is sent to the calling phone.
- The calling phone answers with a 200 – OK
Interference
Connection problems
Does your VoIP device / client have access to the Internet?
Make a “ping” to the registrar domain.
Make a “trace route” to the registrar domain.
To perform a ping / trace route
Do you have a firewall that may not allow/block our services?
Configure the required Firewall-Roles
Are the SIP data configured in your VoIP device / softphone correct?
Check the registrar domain (spelling, the correct country/service).
Check the SIP credentials (spelling, spaces, …).
Is your VoIP device / softphone trying to log in too often?
Adjust the re-register time to 180-300 seconds.
Is another service using / blocking port 5060 (signaling)?
Change the SIP port to 6000.
No audio / One-sided audio
If you have a firewall, our services may not be allowed.
Configure the required Firewall-Roles
One of your network devices (firewall and / or router) has an active SIP ALG. SIP ALG stands for Application Layer Gateway. It checks the VoIP traffic and can modify the SIP packets.
Disable the SIP ALG or the configuration of your VoIP devices to use TLS (if supported).
You have more than one Internet connection.
Your VoIP device / client must send the voice (RTP) over the same Internet connection as the signaling (SIP).
You have enabled sRTP (Encrypted Voice) on your VoIP device / client.
Beide Seiten (VoIP-Gerät / Client und SIP-Leitung) müssen für sRTP konfiguriert sein.
Your telephone handset or microphone is muted. The volume of your speaker is low or muted.
Check your VoIP device / client.
Problems with outgoing calls
You do not have enough credit to make the outgoing call.
Load some credit to your account.
Your VoIP device / client is not registered.
Check the chapter “Troubleshooting «Connection Problems»
They display a number (CLI) that is not allowed on the remote side.
Check the call list in peoplefone portal.
You should see the outgoing call with an error message.
Your account has been suspended for some reason.
Check the peoplefone portal.
Problems with incoming calls
The number is not configured correctly in peoplefone portal.
Make sure you have a valid number (not expired, already ported, …).
Verify that the number is associated with a SIP line to which a VoIP device / software is connected.
Verify that the number is assigned to the SIP line on which your VoIP device / client is registered.
Your VoIP device / client is not registered to the SIP line where the number is assigned.
Überprüfen Sie die Anrufliste im peoplefone Portal.
You should see the incoming call with an error message.
Check the “Troubleshooting” chapter “Connection problems”.
The number is assigned to a SIP line on which call forwarding is configured.
Check the call list in peoplefone portal.
You should see the incoming call and the forwarded outgoing call.
The destination VoIP device / client rejects the call as busy.
Das Ziel-VoIP-Gerät/der Ziel-Client lehnt den Anruf als besetzt ab.
You are already conducting a call. A second call is rejected as busy.
Check your VoIP device / client and disable call waiting.
Incoming calls sometimes do not work.
Check the session timeout in your firewall/router configuration. Make sure that the value exceeds 300 seconds.

